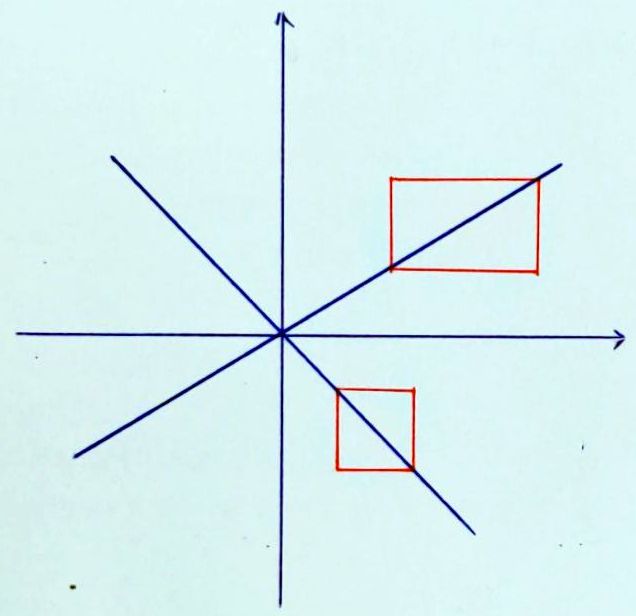
 參閱右圖,
在一條既不水平也不鉛直的直線上任取兩點,可以決定一個由水平、鉛直邊組成的長方形,
使得直線是長方形的對角線。
當直線是通過長方形左下角的對角線,我們說長:寬的比值是直線的斜率
(slope) 或梯度 (gradient);
當直線是通過長方形左上角的對角線,則規定長寬比的相反數是直線的斜率。
參閱右圖,
在一條既不水平也不鉛直的直線上任取兩點,可以決定一個由水平、鉛直邊組成的長方形,
使得直線是長方形的對角線。
當直線是通過長方形左下角的對角線,我們說長:寬的比值是直線的斜率
(slope) 或梯度 (gradient);
當直線是通過長方形左上角的對角線,則規定長寬比的相反數是直線的斜率。
二元一次聯立方程 (system of first degree equations in two unknowns) 當中的個別等式,例如 \(ax+by=c\),本來沒有單獨存在的意義, 直到笛卡耳 (Descartes) 發明了直角坐標,這種等式才有了自己的身分: 直線方程式 (line equation)。
將有序對 (ordered pair) \((x,y)\) 詮釋 (動詞 interpret, 名詞 interpretation) 為坐標平面上的一點, 則無窮多組滿足 (satisfy) 等式 \(ax+by=c\) 的 \(x\) 和 \(y\) 對應坐標平面上無窮多點,它們聚集成一個圖形, 就稱為等式 \(ax+by=c\) 的圖形 (graph of an equation)。 這種可以繪圖的等式稱為方程式,它的「元」稱為變數 (variables), 例如 \(ax+by=c\) 是二元一次方程式 (a first degree equation in two variables), 其中 \(a\), \(b\) 稱為係數 (coefficients),\(c\) 稱為常數項 (constant term)。
根據等量公理,而且在代入法和消去法的程序 (procedure) 中已經實際體驗到: 只要 \(a^\prime:b^\prime:c^\prime = a:b:c\) 而且 \(a^\prime\), \(b^\prime\), \(c^\prime\) 不全為零 (not all zeros), 則 \(a^\prime x+b^\prime y=c^\prime\) 與 \(ax+by=c\) 是相等的等式 (equivalent equations),意思是說滿足它們的無窮多點是同樣的集合, 它們在坐標平面上聚集成同樣的圖形。 在這個意義之下,兩點 \((x_0,y_0)\)、\((x_1,y_1)\) 可以決定唯一一個二元一次方程式。 因為它可以被兩點唯一決定 (determined uniquely by two points), 所以二元一次方程式的圖形就可以定義為直線。
\(x_0\) 可讀作 x sub zero 或 x zero,但是美國口語常說 x naught。 直線 line 的形容詞是 linear,而 linear 譯為「線性」或「線型」。
「數學是發現還是發明?」:
Is Mathematics Invented or Discovered?一直是熱門的哲學問題; 其他數學或許是發現 (discovery),但直線方程式實在是發明 (invention)。
水平是 horizontal,鉛直是 vertical;例如
\(x\) 坐標是水平的,\(y\) 坐標是鉛直的。在坐標平面上,與 \(x\) 坐標平行的直線都稱為水平的, 與 \(y\) 坐標平行的直線都稱為鉛直的。
The \(x\) axis is horizontal and the \(y\) axis is vertical.
 參閱右圖,
在一條既不水平也不鉛直的直線上任取兩點,可以決定一個由水平、鉛直邊組成的長方形,
使得直線是長方形的對角線。
當直線是通過長方形左下角的對角線,我們說長:寬的比值是直線的斜率
(slope) 或梯度 (gradient);
當直線是通過長方形左上角的對角線,則規定長寬比的相反數是直線的斜率。
參閱右圖,
在一條既不水平也不鉛直的直線上任取兩點,可以決定一個由水平、鉛直邊組成的長方形,
使得直線是長方形的對角線。
當直線是通過長方形左下角的對角線,我們說長:寬的比值是直線的斜率
(slope) 或梯度 (gradient);
當直線是通過長方形左上角的對角線,則規定長寬比的相反數是直線的斜率。
水平線的斜率是零,鉛直線沒有斜率。斜率相等的直線彼此重疊或平行 (parallel), 斜率互為相反倒數 (opposite reciprocals) 的兩直線互相垂直 (perpendicular)。
The slope of a horizontal line is 0, and the vertical lines have no slopes.
\(x\) 截距和 \(y\) 截距分別是 \(x\)-intercept 和 \(y\)-intercept。 直線與 \(x\) 軸正向 (the positive direction of the \(x\) axis) 所夾的有向角 (directed angle) 稱為傾角 (angle of inclination), 斜率等於傾角的正切:
The slope equals the tangent of the angle of inclination.當斜率為正,直線與 \(x\) 軸正向所夾的銳角稱為仰角 (elevation angle / angle of elevation),當斜率為負,那個銳角則稱為俯角 (angle of depression)。
| [語音講解:line-eq.mp3] |